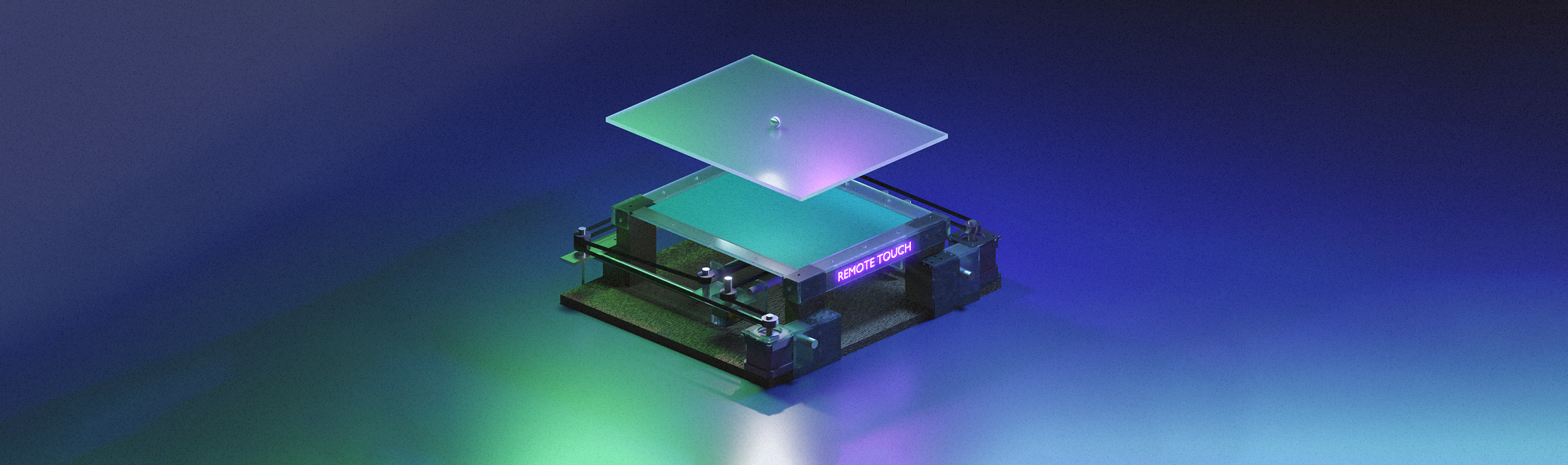
Remote Touch: Tangible Computing to Share Touches
April 2021
Introduction
As physical distances between people increase every passing day, ways to connect people remotely satisfy the visual and auditory sensories, but fall short on a crucial front- the intimate feeling of touch.
This project proposes and presents ‘Remote Touch’, a device capable of remotely sending and receiving personalised and intimate touch patterns, and more.
India HCI Research PaperExploring Tangible Interactions
Brainstorming sessions to find lesser explored areas in the realm of tangible interactions.
Explorations
Some directions were explored in the initial phases, mainly focussing on touch and taste.
The Proposal
Remote Touch: A device that simulates your partner’s finger moving across your palm.
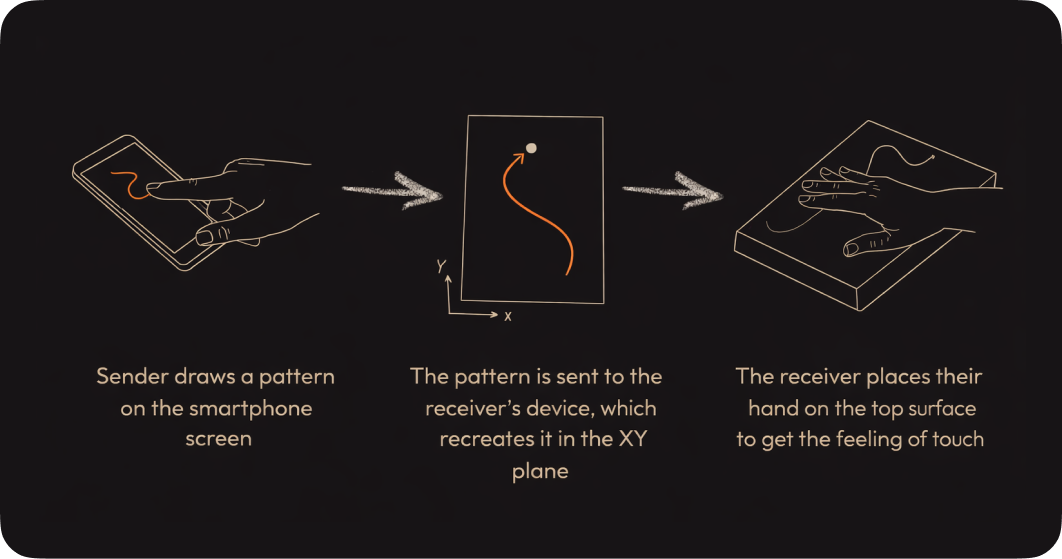
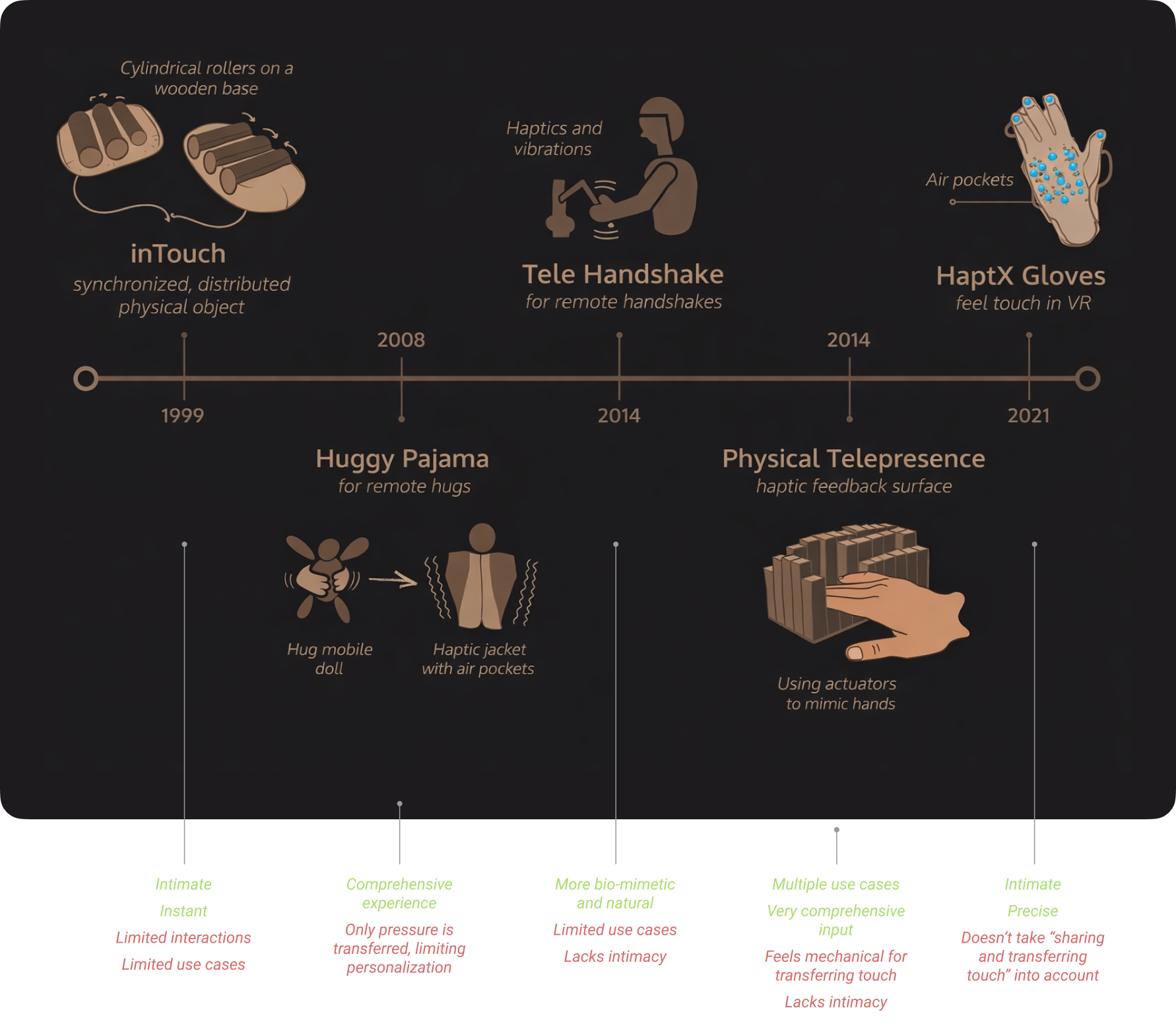
State of the Art
Researching the explorations already done in the field over time.
Product Placement
The product combines freedom of movement offered by 2 axis CNC technology with the ability to capture, transfer and express touches; providing an experience that’s:
...while being open to multiple other use cases.
Usage Scenario
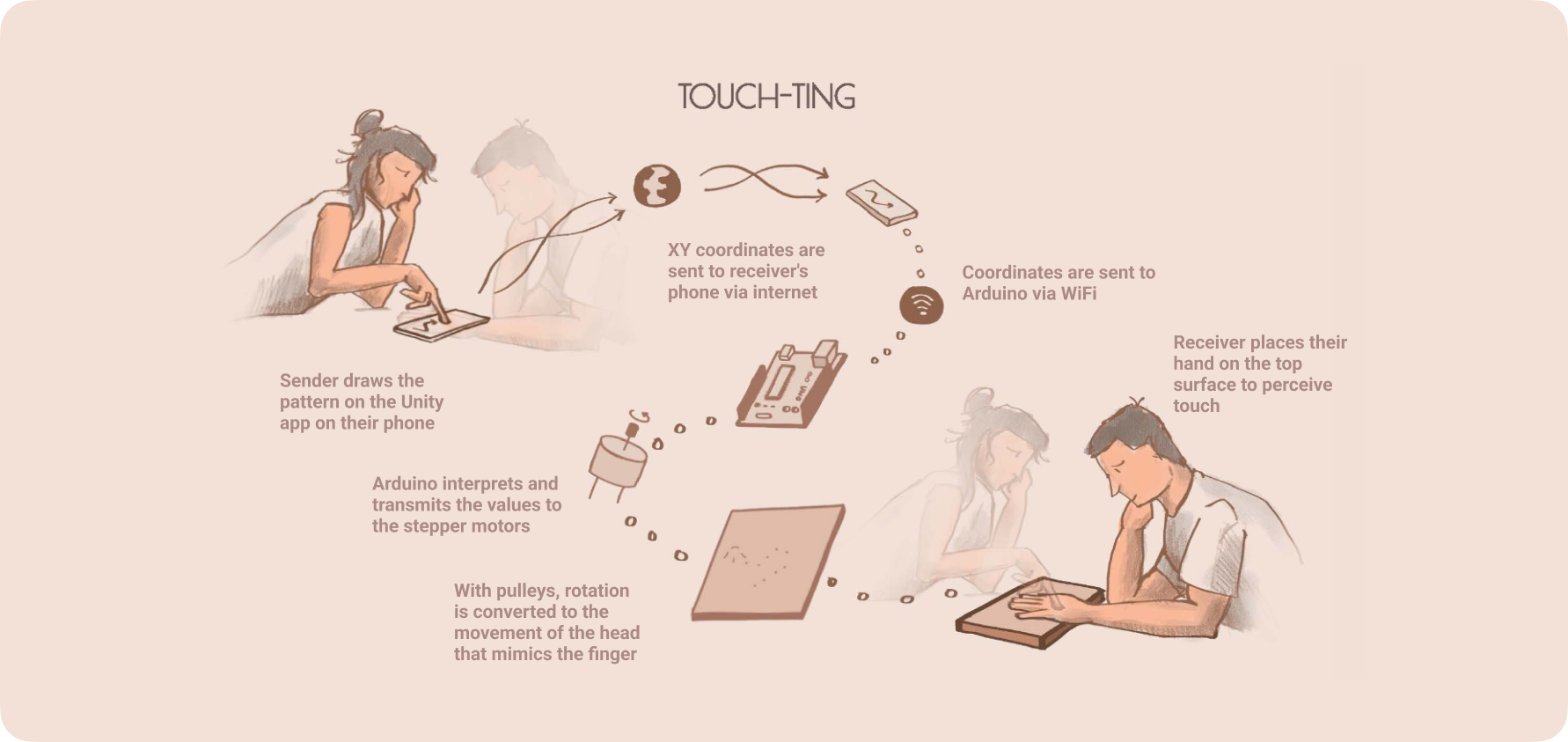
Touch-ting
Introducing touch-ting: texting, but with touch.
Other use cases
Remote touch can also be used for some other use cases, like drawing, sand art, or simple installations.
Designing the Device
The design process consisted of figuring out the hardware, electronics and the software involved in touch-ting.
Hardware Backend
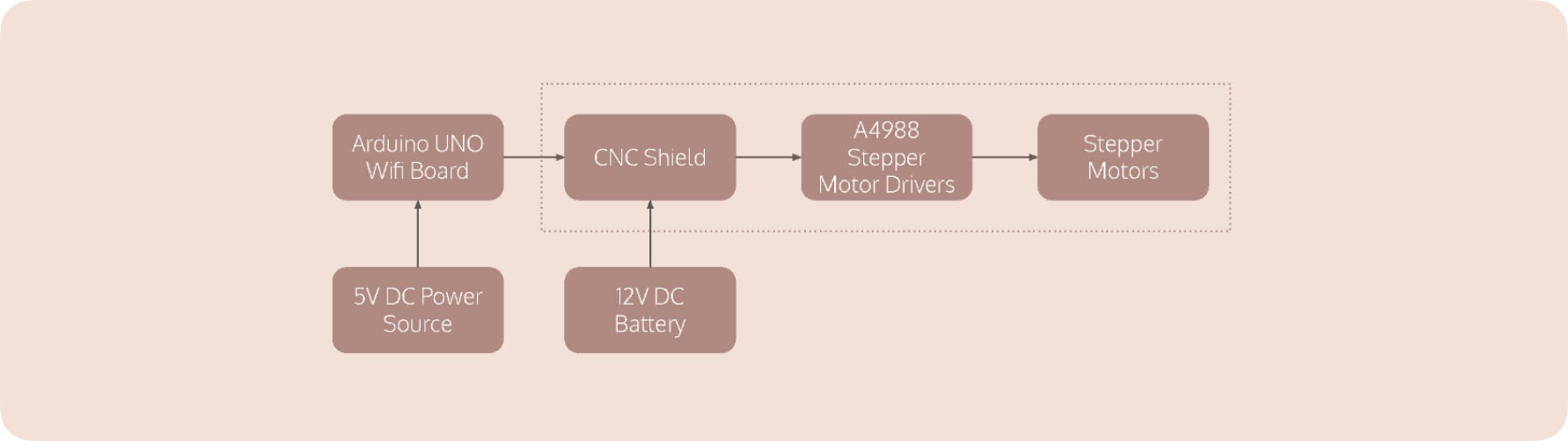
The hardware consists of 2 stepper motors moving a central ‘head’ using a system of pulleys. The head is mounded with a neodymium magnet.
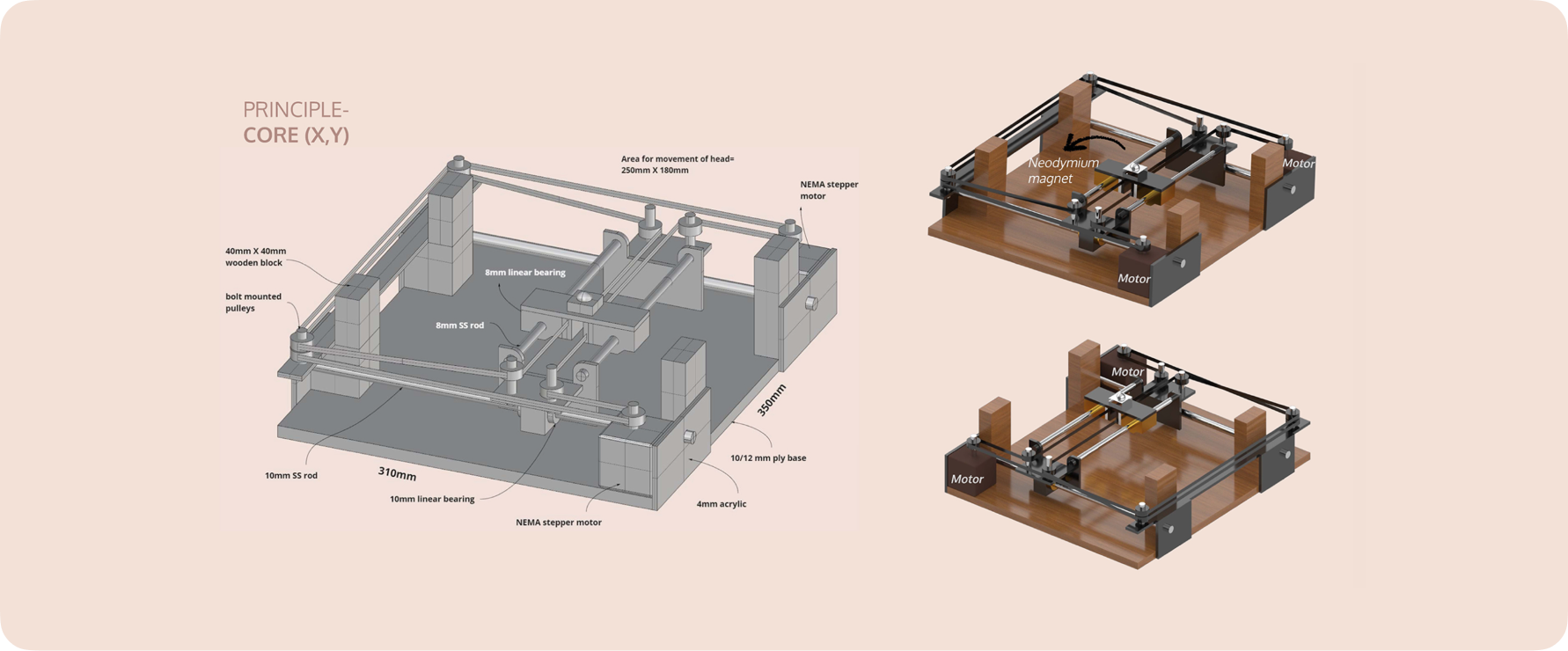
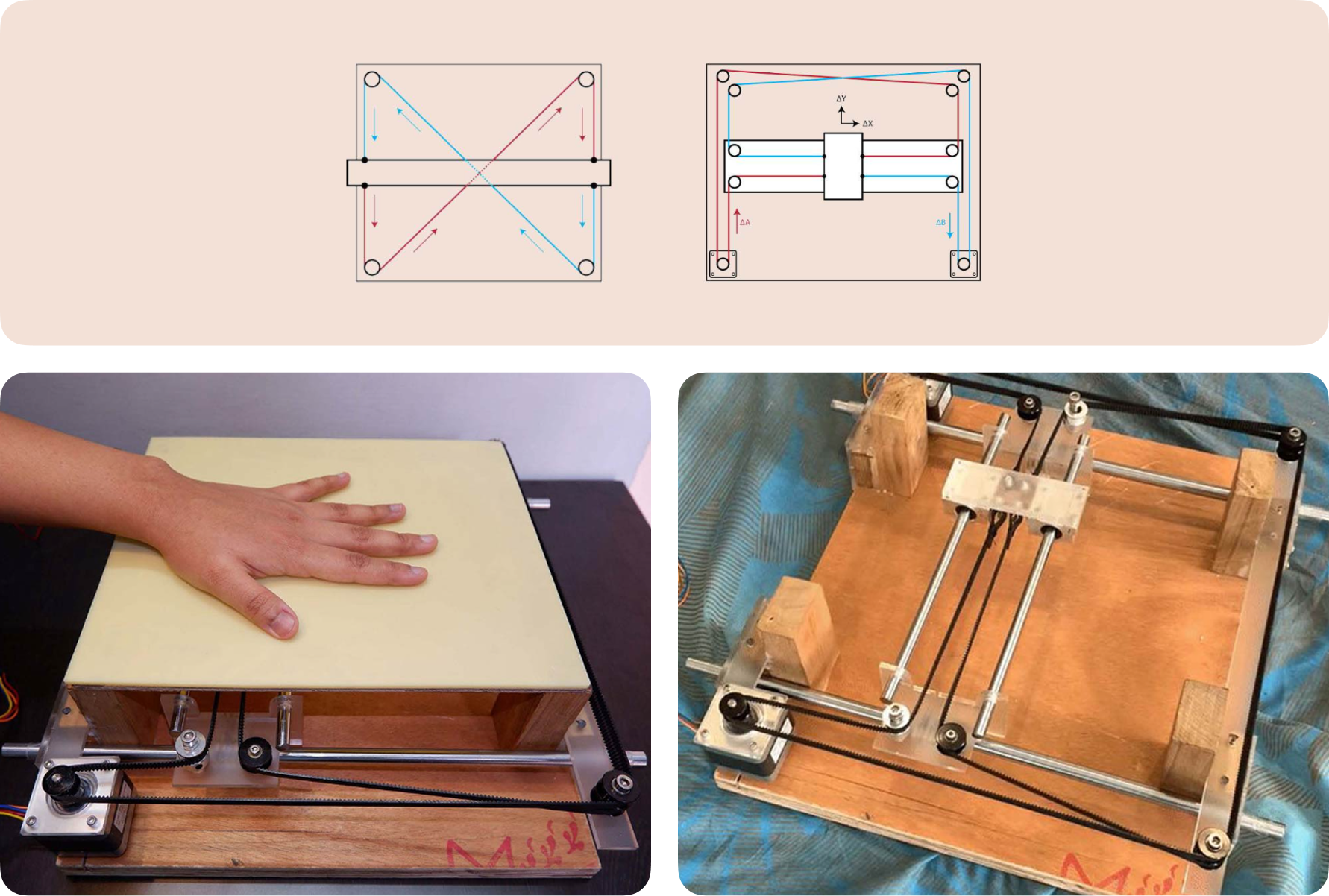
The pulley system is based on the Core XY principle similar to a standard drafting table, where rotating both motors in the same direction produces horizontal motion, while rotating both motors in opposite directions produces vertical motion.
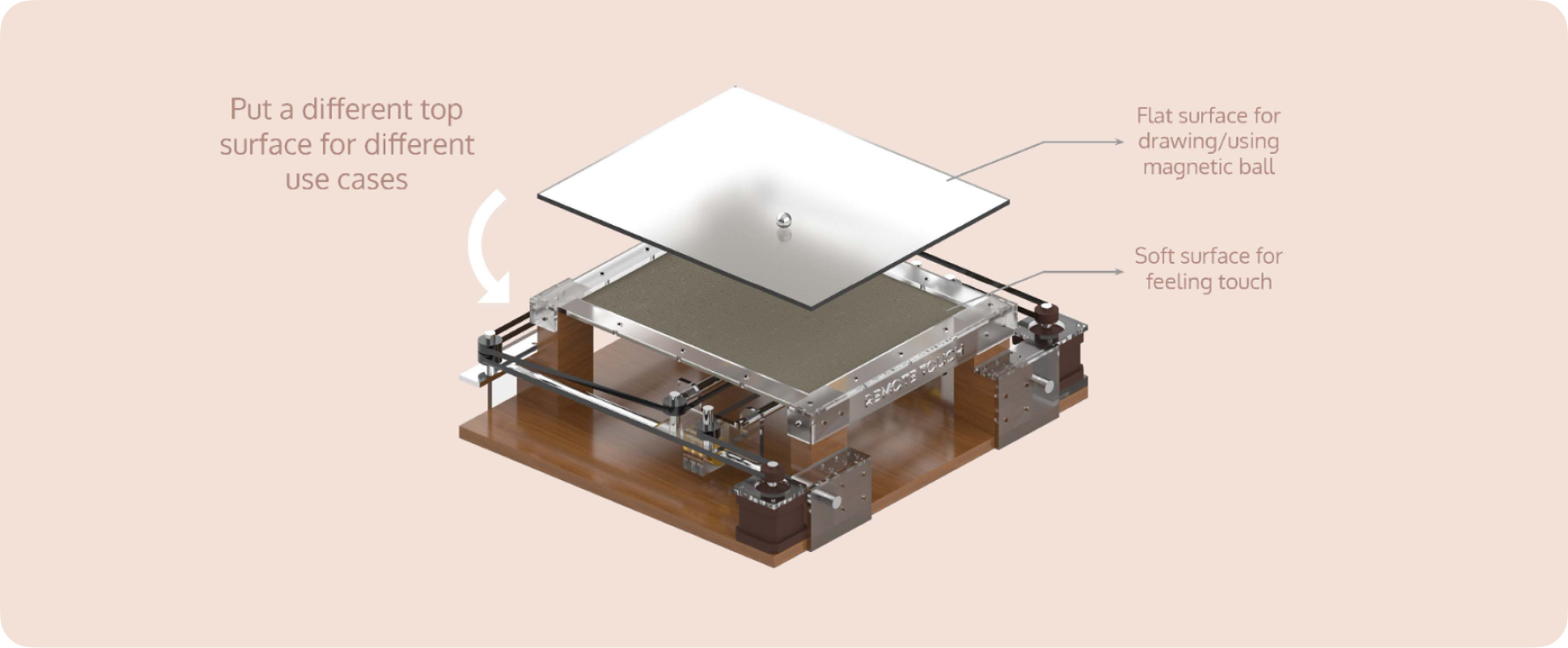
Hardware Frontend
The device can be covered by either a soft surface suitable for feeling touches, or a hard acrylic sheet that can be used for other use cases mentioned above. For getting the feeling of touch, we chose tattoo practice skin, since it feels the closest to actual human skin.
Software and Electronics
Functional Mapping
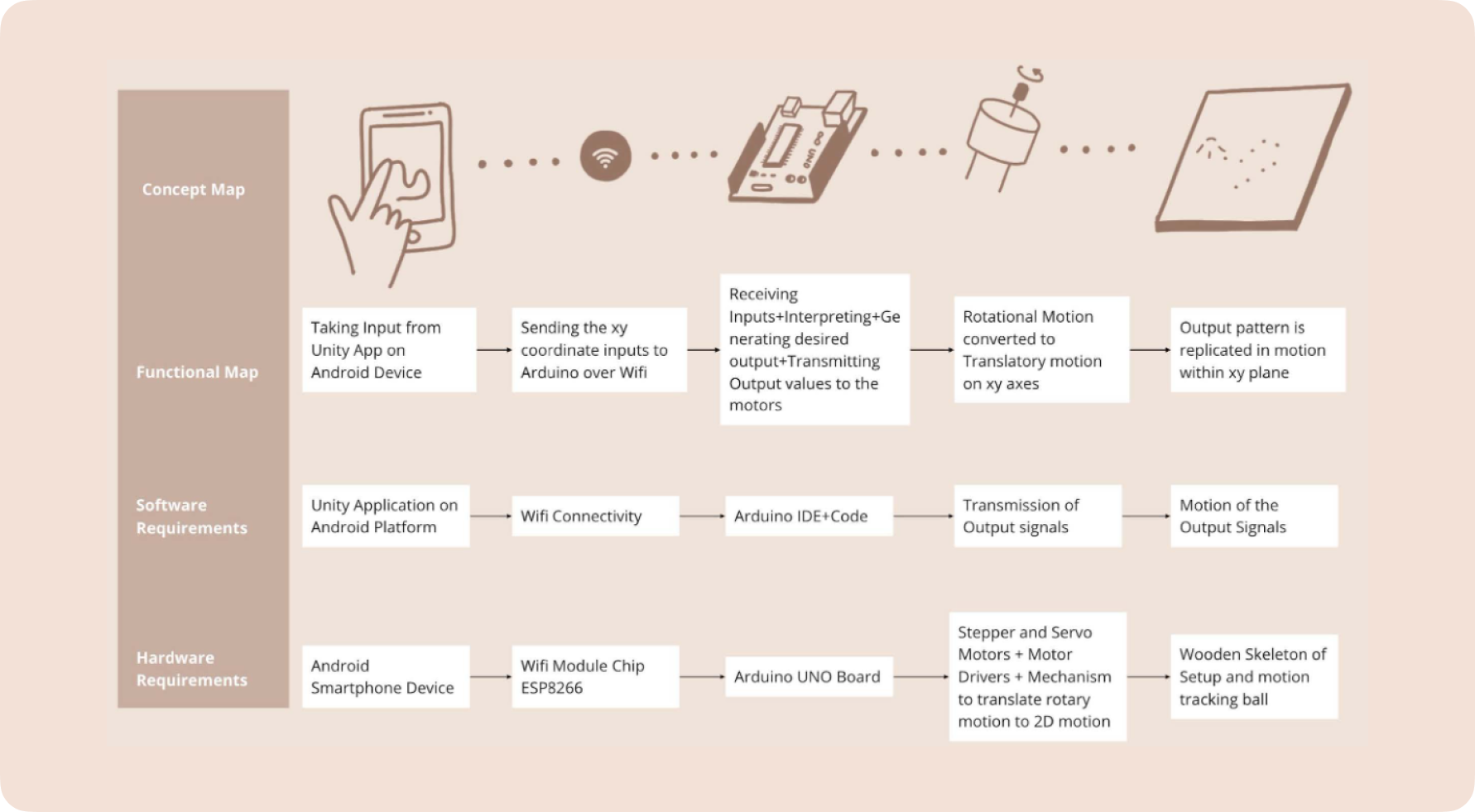
Circuit Diagram
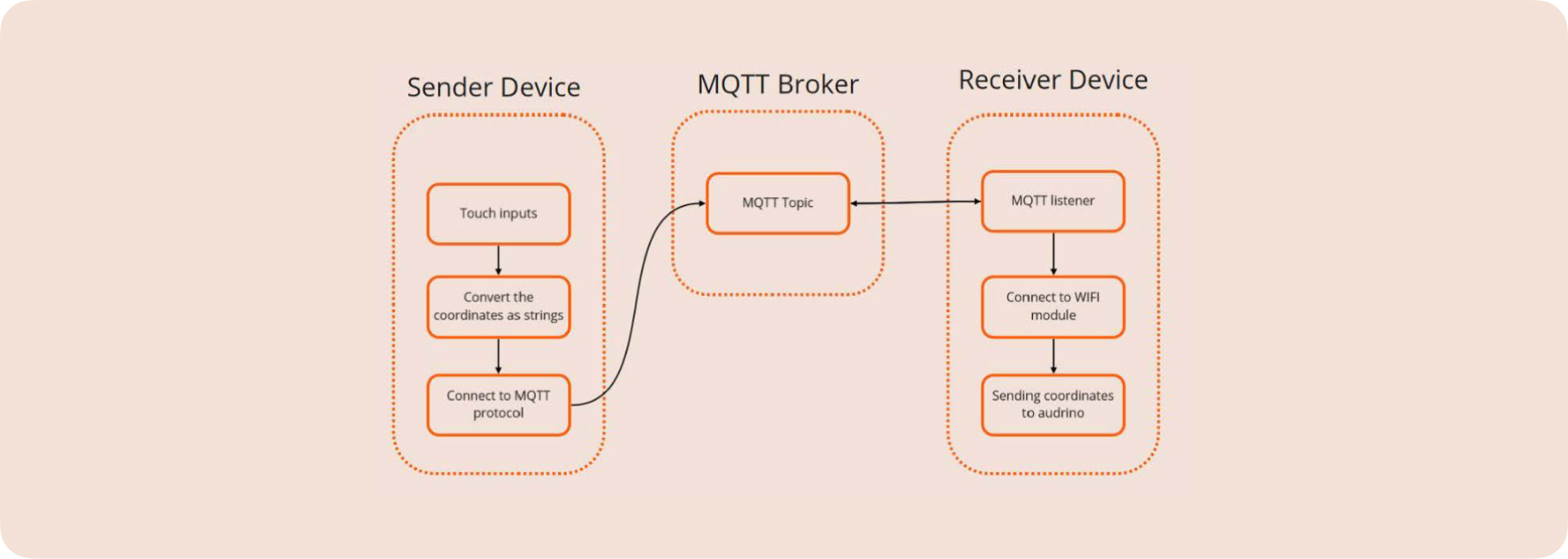
Remote Connection
Limitations & Future Scope
- The magnet head can be moved in the Z axis with an actuator, increasing personalisation by communicating pressure
- Can make the output surface touch sensitive, negating the need to use the phone separately
- A visual cue could be given to the sender regarding the receiver’s hand position, increasing engagement
- A custom PCB with motors designed specifically for this product will remove some problems like lag from Arduino
Check out the detailed project report.